More than 34 million people in the United States have diabetes, and 1 in 5 of them don’t know they have it.* According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, diabetes can affect almost every part of your body and understanding how to manage diabetes can improve your health and reduce your risk for developing other health complications. Ani Narinyan, Outpatient Pharmacist at CHA HPMC, explains the condition and shares helpful management tips.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that results in too much sugar in the blood, causing health problems over time.
Why is it important to take care of your diabetes?
It is important to manage your blood sugars in order to prevent long term consequences and complications of diabetes such as heart disease, kidney disease, eye disease/blindness, and nerve damage (loss of sensation in the hands and feet).
What are the different types of diabetes?
There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1: A chronic condition, also known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Type 2: A condition in which either the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or the body doesn’t respond to the insulin that is produced—which means it can’t use up the sugar in the body, or can be combination of both. Type 2 diabetes can be genetic or developed over time, and presents during later adulthood.
How is this condition diagnosed?
Diabetes can be diagnosed in various ways:
Blood tests
- Fasting blood sugar
- 2 hours oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- Hemoglobin A1C: Which measures diet sugar exposure over the past 3 months.
- Normal is < 5.7 %
- Pre-diabetic 5.7 – 6.4 %
- Diabetic > 6.5 %
Clinical symptoms which may indicate high sugar levels include:
- Frequent urination, extreme thirst and hunger, dry skin, blurry vision, slow wound healing. (Please note that clinical symptoms aren’t enough to diagnose the condition and further testing needs to be done.)
How do pharmacists help patients with diabetes management?
CHA HPMC pharmacists help educate and inform patients on effectively managing diabetes in the following ways:
- Improve and promote compliance with medications
- Educate self-administration of insulin and other injectable medications
- Educate and support blood sugar monitoring
- Identify and resolve drug-related side effects (example: Hypoglycemia)
- Identify and communicate with health care provider on adjustments needed to current therapy
- Provide education on how to reduce health risks associated with diabetes
What are some of the ways to manage diabetes?
While type 1 diabetes cannot be completely cured and requires a treatment plan, type 2 diabetes can be reversed by following a healthy lifestyle.
Diet – What you eat will effect your blood sugar and it is a key aspect when managing diabetes.
- Eat nutrient-dense food that’s rich in fiber, vitamins and minerals, and low in added sugars, sodium and unhealthy fats.
- Reduce refined carbs (white rice, bread, pastries, etc.), refined sugar (high fructose corn syrup, fruit juice with added sugar, etc.), processed food, and junk food. It is difficult for the body to break down these types of foods due to the lack of enough insulin thus leading to increased blood sugar levels.
- Substitute your meat options for fish 2-3 times a week.
- Include plant-based proteins such as black beans, or lentils.
- Choose lean cuts of meat.
- Substitute refined carbs with whole wheat options.
- Try using more quinoa, barley, bulgur, buckwheat.
- Pick non-starchy vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, or salad.
- Choose dark green and dark yellow vegetables such as kale, brussel sprouts, spinach, squash, and peppers.
- It is better to boil, bake, roast, steam or grill when cooking.
- Use nonstick pans to avoid adding more fats and oils.
- Trim the fats off meats before cooking.
- Use healthy oils when cooking such as olive or avocado oil.
- Control portion size of each type of food as shown below.
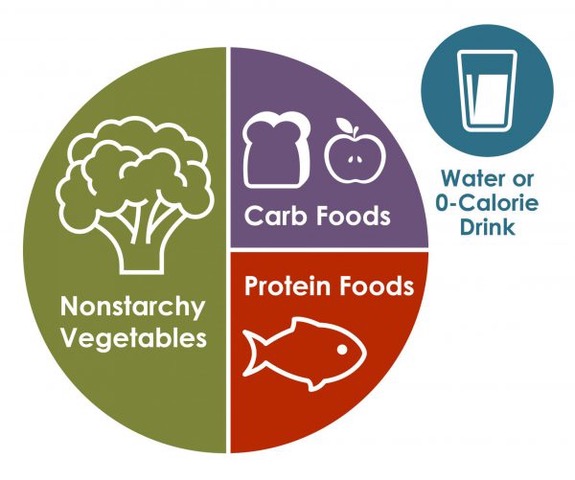
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Exercise: Exercise is another important component in managing diabetes. Regular exercise can help lower your risk for heart attack and stroke, stimulate insulin activity, stengthen bones and muscles, and overall stess relief. Types of excercises include:
- Aerobic exercise (power walking, running, swimming, or dancing): Beneficial for lowering risk of heart disease, improving blood circulation, strengthening bones and heart, as well as helping you reach your target goals of blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. It is advisable to do 30 minutes per day for 5 times a week or 150 minutes per week.
- Strength training (lifting light weights, or exercising with elastic bands): Helps strengthen muscles, burn more calories as well as helps promote insulin functioning. It is advisable to perform strength training 3 times per week.
Annual exams:
- Foot Exam: Diabetes can lead to nerve damage which can result in poor sensation in feet and lead to an unnoticed sore causing infections and eventual amputation if it is not treated promptly.
- Eye Exam: Over time, diabetes can cause damage to your eyes that can lead to poor vision or even blindness. But you can take steps to prevent diabetic eye disease, or keep it from getting worse, by taking care of your diabetes and maintaining regular check-ups with your eye doctor.
Keep a diary / log book
- Document what you eat, how much you ate, and how much you exercised.
- Important to monitor blood sugar with a glucometer and write down the levels daily and share with your doctor during visits. This will help your doctor in making proper changes to your care plan in order to improve your daily sugar levels.
- It’s important to know the ideal blood sugar levels:
- Blood sugar before meals or after waking (fasting) : 80-130 mg/dL
- Blood sugar 2 hours after a meal : <180 mg/dL
- Hemoglobin A1C: <7%
- If your blood sugar levels are consistently high, call your doctor.
- If your blood sugar level is 70 mg/dl or below:
- Step 1: Treat with either: a. Half-cup of juice or regular soda (not diet); b. 3 or 4 glucose tablets; c. 6 or 7 hard candies; d. 1 tablespoon of sugar or honey
- Step 2: Check blood sugar again in 15 minutes. If your blood sugar is still below 70 mg/dl repeat step 1 and contact your doctor. If you experience low blood sugar often, talk to your doctor.
Supplements
- Take soluble fiber supplement which helps slow down absorption of sugar.
- It can also help with heart health, digestive system, and reduce cholesterol
- Be sure to drink 6-8 oz. of water daily to prevent constipation
- Recommended amount of daily fiber per American Diabetes Association is 25g/day for women and 38 g/day for men
- For people taking Metformin, Vitamin B12 is great supplement to take, because Metformin can deplete your Vitamin B12. Please consult your doctor to check your B12 levels before starting the supplement.
For more tips and helpful information on diabetes management, please visit American Diabetes Association at www.diabetes.org.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fast Facts. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/quick-facts.html
 ENGLISH
ENGLISH KOREAN
KOREAN Spanish
Spanish RUSSIAN
RUSSIAN Armenian
Armenian FILIPINO
FILIPINO Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional)

최신댓글